Using data to automate your communication can only go so far when you’re asking someone to fill out a form, but a lot of people lose sight of one of the best ways to collect customer data: by tracking customer behaviour. Below are some examples of customer behaviour that you can track to support your communication automation.

List Subscription
This starts a workflow when a customer is added to a list in your database (e.g.: your newsletter database).
Use this to start or end a customer’s communication journey. Here are some examples:
- Nurturing new leads
- Onboarding new customers
- Engaging with and upselling to existing customers
- Educational campaigns
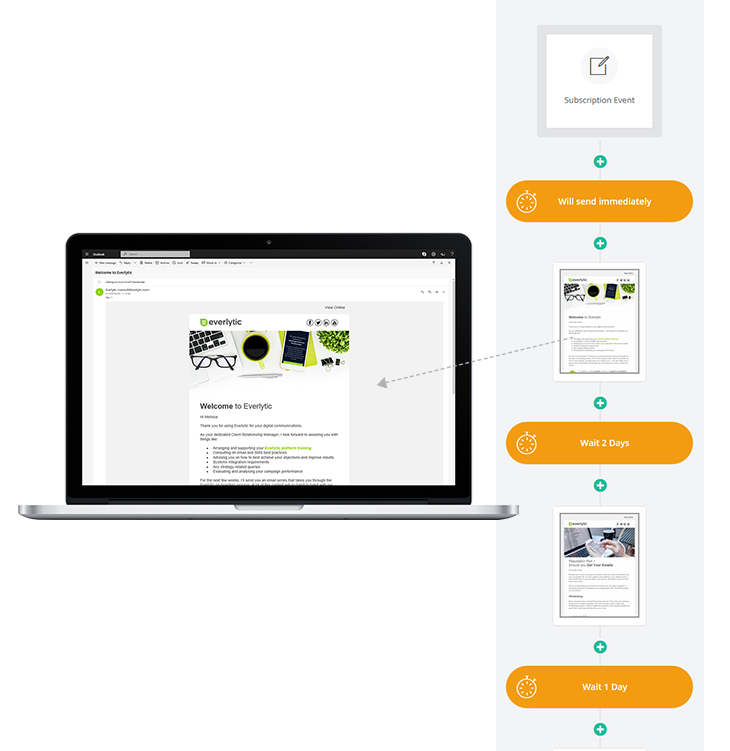
Everlytic Onboarding Series
At Everlytic, we use a 10-email workflow to onboard all new clients to our platform. It sends dynamic content depending on what package the client is on and, if the client has a Relationship Manager, it sends from the relevant Relationship Manager’s email address.
This helps us automate and personalise the onboarding process, saving us time, and ensuring that every new client gets the tools they need to get started.
Email / SMS Engagement
This triggers a workflow when a customer reads or clicks on a link in one of your emails or SMSs. This trigger is very flexible because you can specify the exact email / SMS and apply it to a specific link in that message. You can also apply a filter to apply to a specific list of customers.
Use this to:
- Track customer engagement
- Set a condition, so customers who engage go down a specific path
- Update the customer’s data and segment your list
- Trigger follow-up messages (“You didn’t sign up for the webinar…”)
By tracking engagement, you can start tracking your audience’s interests without needing them to fill out a form to tell you. This helps you get the most out of your existing customers, keeping them engaged, and upselling them on products and services they like the most.
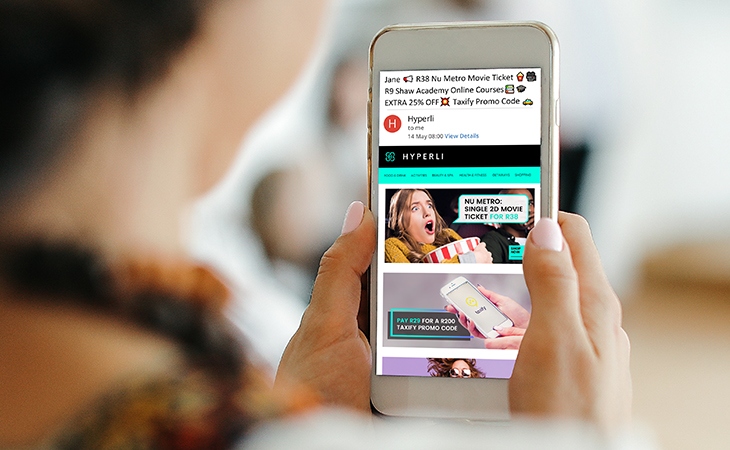
Hyperli Re-Engages Inactive Customers
Hyperli comes at engagement from a different angle: by tracking which customers aren’t engaged. This enables them to send enticing campaigns just to these audiences, bringing cold customers back to life. Read the case study.
Landing Page Engagement
Landing pages are often used as extensions of your email campaign. You can track if a customer views, doesn’t view, clicks, or doesn’t click on the content on your landing page and use that to automatically trigger customised messages.
Use this to:
- Send triggered communications based on a customer’s engagement on a landing page
- Update a custom field with customers’ interests
Create Customised Journeys Based on Your Customers’ Page Views
Your business is multi-dimensional. To connect with customers on the topics and pain points that mean the most to them, bundle the content you have on these subjects and trigger customised messages when they land on specific landing pages.
For example, if one of your customers views a landing page for an eye-care product, you can trigger a mail with more eye-care content and benefits, related products, or services that you have available.

Field Change
Use this to trigger an action when a data field is updated. It works if a field on an existing customer changes to or from any value (including empty fields) or a value that you specify. It also works well for sending follow-up sequences and notifying people in your organisation that the field has been updated.
Use this to:
- Send follow-up messages based on the updated field
- Inform people in your business that a field has changed
- Add a customer to another workflow, customising the journey according to their position in the funnel
Shares, Forwards, or Replies
Some systems enable you to trigger a workflow when your email is forwarded, replied to, or shared on social media.
Use this to:
- Inform people in your business that the message was shared
- Thank the customer for sharing your message
- Introduce the customer to your referral programme
- Tag someone as a brand advocate

Dynamic Data Sets
This is an advanced workflow type that allows a customer to exist in the workflow multiple times via API, holding unique data per entry.
Dynamic Data Sets Workflow Example
If a client purchases a flight from an airline company, they can get added to a workflow and the unique data set fields are flight reservation number and departure date. The client flows through the workflow receiving the necessary information for those data sets.
The same client can then purchase another flight and get added to the same workflow, but this time the reservation number and departure dates will be different. Both versions of this customer can exist in the same workflow and receive customised emails and SMSs based on each set of unique data.
Use this for license renewals, doctors’ appointments, or any sequence where you can receive similar communications, but the data is specific to the customer at that time.












